

It also involves the use of simple procedures and formulas. At this level, subject matter content involves working with facts, terms, and properties of objects. The higher the level, the more complex and more steps required to complete the task.Įlements that fall into this category involve tasks that require students to reproduce or recall knowledge and skills. Educators are applying DOK to design better instruction. The model has since expanded to include language, arts, history, social studies, mathematics, and science. Originally, Webb developed Depth of Knowledge for science and math standards. This concept was developed by Norman Webb. More than that, though, DOK changes academic rigor and better prepares students for real-world experiences in ways that other critical thinking systems haven’t done.Depth of Knowledge (DOK) is the complexity of understanding required to answer an assessment-related item or classroom activity. Ultimately, Webb’s Depth of Knowledge alludes to the depth of understanding necessary for completing learning tasks and answering complex questions. In each level of Webb’s Depth of Knowledge, students place learning in context.

The final step would be to come up with a solution that will save the turtles and remove them from the endangered species list. Level 4 happens when students can synthesize the aggregation of all four steps. In this level, the teacher might ask students to write a persuasive essay convincing others to save the Leatherback Sea Turtle.īy the time students get to the fourth level, they are ready to apply what they’ve learned to real-world problems that are both authentic and challenging. They consider not only their findings, but also the perceptions or prejudices of others. The third level of DOK requires complex thinking involving analysis and evaluation. Now they must figure out what’s important and how they can use their findings. In the case of the sea turtle, students already have the facts. This level help students identify relationships between topics and details. Then they look for ways to solve multi-step problems requiring inference and interpretation. In the second level, students determine how they can use the information. Knowledge and recall are critical for Level 1.ĭOK Level 2: Why is this important, and how can we use it? Then they would present their findings to classmates.īy asking low-level questions, the teacher gets students to recall information. They would gather all the facts about the turtles they could find. This initial work establishes a foundation for all other related learning.įor example, imagine that students are studying the Leatherback Sea Turtle. These four DOK levels change academic rigor.Īt the lowest DOK level, students gather information and directions. Teachers must consider context as they scaffold lessons according to each level in Webb’s Depth of Knowledge. Knowing which verb best describes a particular learning activity is no longer enough to address rigor. Implementing DOK requires that teachers plan their lessons carefully. Teachers who incorporate Webb’s Depth of Knowledge increase the levels of academic rigor in their classrooms.

Students must activate knowledge and experience at teach level to be successful learners. As the context changes, so do the levels of understanding and rigor. The difference between Webb’s Depth of Knowledge and Bloom’s Taxonomy or Marzano’s Essentials for Rigor is the student’s frame of reference. Teachers seeking ways to help students think critically in complex situations turn to Webb’s Depth of Knowledge. Norman Webb, DOK scaffolds learning experiences to give students footholds in increasing academic rigor.ĭOK builds a path to real-world competency. DOK, however, increases academic rigor by focusing on context.
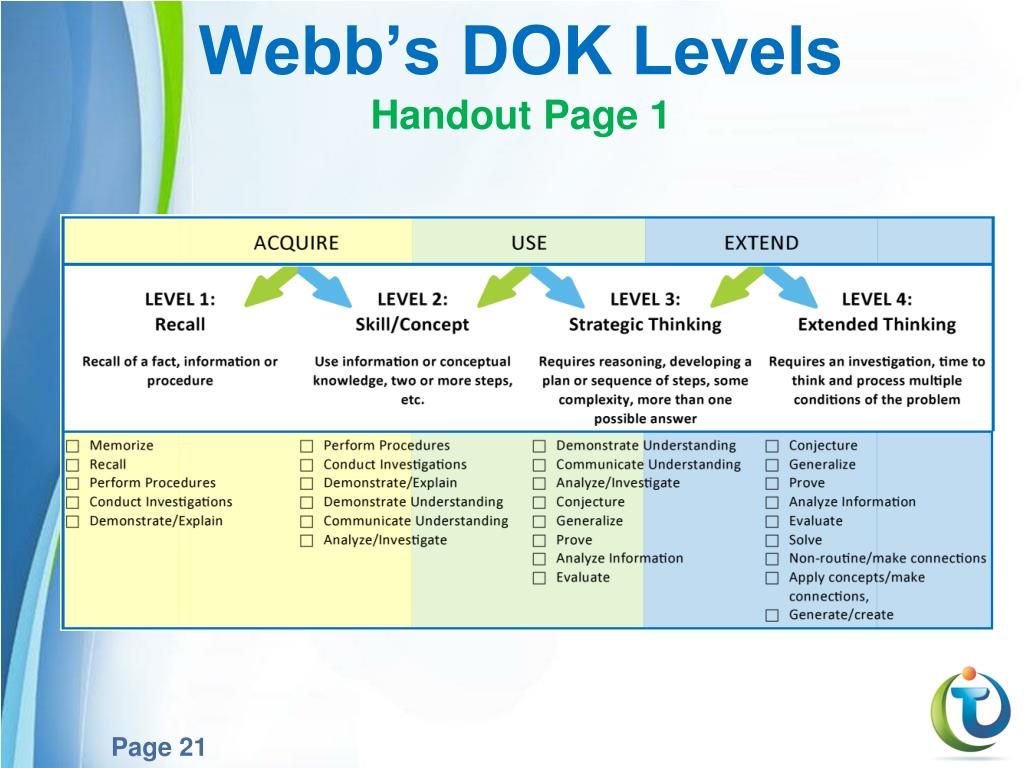
Students engaged in isolated activities that did not consistently require advanced thinking. Previous attempts to identify and apply the steps required for higher order thinking fell short. DOK goes beyond identifying the type of thinking required for a learning activity. Webb’s Depth of Knowledge (DOK) increases learning rigor.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
